As winter sets in and daylight becomes a precious commodity, many individuals find themselves grappling with Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD). This form of depression, commonly known as the winter blues, is directly linked to the changes in seasons, particularly the reduced exposure to sunlight.
However, there’s good news—there are numerous strategies to manage and alleviate the symptoms of SAD, allowing you to embrace the winter season with a positive mindset.
Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder
Seasonal Affective Disorder is a subtype of major depressive disorder that occurs at specific times of the year, most commonly during the fall and winter months when sunlight exposure is limited.
The exact cause of SAD is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to the disruption of the body’s internal clock (circadian rhythm) and changes in serotonin and melatonin levels.
Symptoms of Seasonal Affective Disorder
Symptoms of SAD are similar to those of major depressive disorder and may include:
- Depressed mood: Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or a general sense of emptiness.
- Loss of interest or pleasure: Decreased interest in activities that were once enjoyable.
- Low energy: Fatigue or a sense of being physically drained, even after a good night’s sleep.
- Changes in sleep patterns: Insomnia or oversleeping can occur, and there may be difficulty in maintaining a regular sleep schedule.
- Changes in appetite or weight: Increased cravings for carbohydrates and weight gain are common, but some people may experience a decrease in appetite and weight loss.
- Difficulty concentrating: Trouble focusing on tasks, making decisions, or remembering things.
- Feelings of worthlessness or guilt: Negative thoughts about oneself, with an exaggerated sense of guilt or self-blame.
- Social withdrawal: A tendency to avoid social interactions and isolate oneself from friends and family.
- Irritability: Increased irritability and a shorter temper than usual.
- Physical symptoms: Some individuals may experience physical symptoms such as headaches, body aches, and digestive problems.
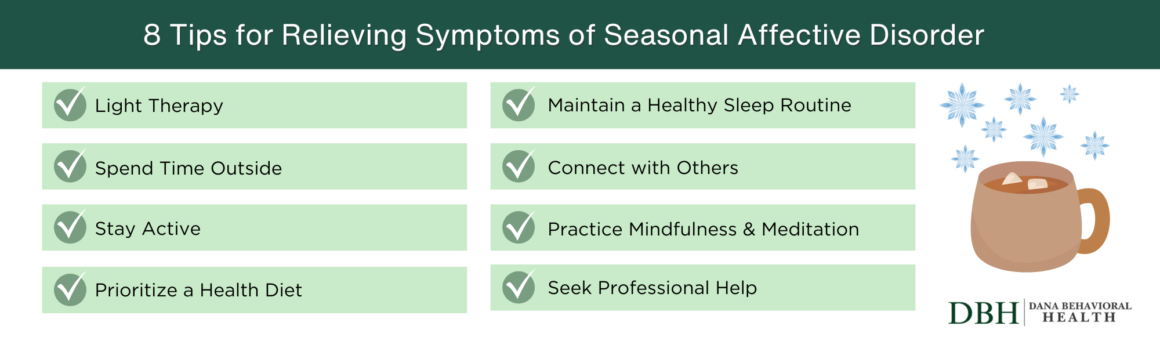
Tips for Relieving Symptoms of Seasonal Affective Disorder
While these symptoms can be challenging, there are several proactive steps you can take to manage SAD and enhance your well-being during the winter season.
Light Therapy
One of the most effective treatments for SAD is light therapy, also known as phototherapy. This involves exposing yourself to a bright light that mimics natural sunlight for a specified amount of time each day.
Light therapy helps regulate your circadian rhythm and boosts serotonin levels, alleviating symptoms of depression. Invest in a lightbox with at least 10,000 lux of light intensity, and position it at eye level about 16 to 24 inches away from your face for optimal results.
Maximize Natural Light Exposure
Make the most of the limited daylight hours by spending time outdoors. Take short walks during lunch breaks, open curtains wide to let sunlight into your home or workspace, and position your desk near windows.
Exposure to natural light, even on cloudy days, can positively impact your mood and help regulate your sleep-wake cycle.
Stay Active
Regular physical activity is a powerful antidote to depression, including SAD. Engage in activities you enjoy, whether it’s indoor exercise classes, outdoor sports, or simple home workouts. Exercise releases endorphins, the body’s natural mood elevators, helping to combat feelings of lethargy and sadness associated with SAD.
Prioritize a Healthy Diet
The winter months often bring cravings for comfort foods, but it’s crucial to maintain a balanced and nutritious diet. Consume foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, which have been shown to have mood-boosting effects.
Additionally, avoid excessive caffeine and sugar intake, as they can contribute to energy crashes and worsen depressive symptoms.
Establish a Consistent Sleep Routine
Disruptions in sleep patterns are a common symptom of SAD. Aim for a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day. Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down.
Avoid electronic devices before bedtime, as the blue light emitted can interfere with melatonin production and disrupt your sleep.
Connect with Others
Social isolation can exacerbate feelings of depression, so make a conscious effort to connect with friends and family. Plan social activities, whether virtual or in-person, and share your feelings with loved ones. Supportive relationships play a crucial role in managing mental health, providing a sense of connection and understanding.
Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Incorporate mindfulness and relaxation techniques into your daily routine to reduce stress and improve your mental well-being. Activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help calm your mind and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression associated with SAD.
While Seasonal Affective Disorder may cast a shadow over the winter months, there are practical and effective strategies to manage its impact on your mental health. By incorporating light therapy, maximizing natural light exposure, staying active, maintaining a healthy diet, establishing a consistent sleep routine, connecting with others, and practicing mindfulness, you can navigate the winter season with resilience and embrace the unique beauty it has to offer.
Remember, seeking professional help is always an option if your symptoms persist or worsen. With the right tools and support, you can conquer the winter blues and cultivate a positive and fulfilling winter experience.
