Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy represents a significant advancement in the treatment of depression, depressive anxiety, and OCD.
This innovative technique utilizes magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain, offering hope to individuals for whom medication has been ineffective, or for those who cannot tolerate the side effects of antidepressant medication.
In this blog post, we will explore the mechanics of TMS therapy, its applications, benefits, considerations, and the future potential of this fascinating breakthrough in mental health treatment.
Understanding TMS Therapy
TMS therapy is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic pulses to target specific areas of the brain associated with mood regulation.
The device, which is placed on the scalp, generates a magnetic field that induces a small electric current in the underlying brain tissue, stimulating brain cells in the targeted region.
This stimulation is believed to activate regions of the brain that have decreased activity in depression and other mental health disorders.
The Science Behind TMS
The exact mechanisms by which TMS exerts its therapeutic effects are still being studied, but it is generally believed to involve the modulation of neurotransmitter levels, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which play critical roles in mood regulation.
By stimulating areas of the brain involved in mood control, TMS can help alleviate symptoms in patients with depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions.
What Conditions Does TMS Therapy Treat?
While TMS is most commonly associated with the treatment of major depressive disorder, especially in cases where patients have not responded to antidepressants, its applications are expanding.
Research has shown that TMS can be effective in treating anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) as well. Research has also shown potential in its application for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and even neurological conditions such as stroke rehabilitation and Parkinson’s disease.
One of the most compelling aspects of TMS therapy is that it is non-invasive, does not require sedation, and patients can resume their normal activities immediately after each session.
Moreover, TMS has a favorable side effect profile, with the most common side effects being scalp discomfort during sessions and mild headaches.
What a Typical TMS Session is Like
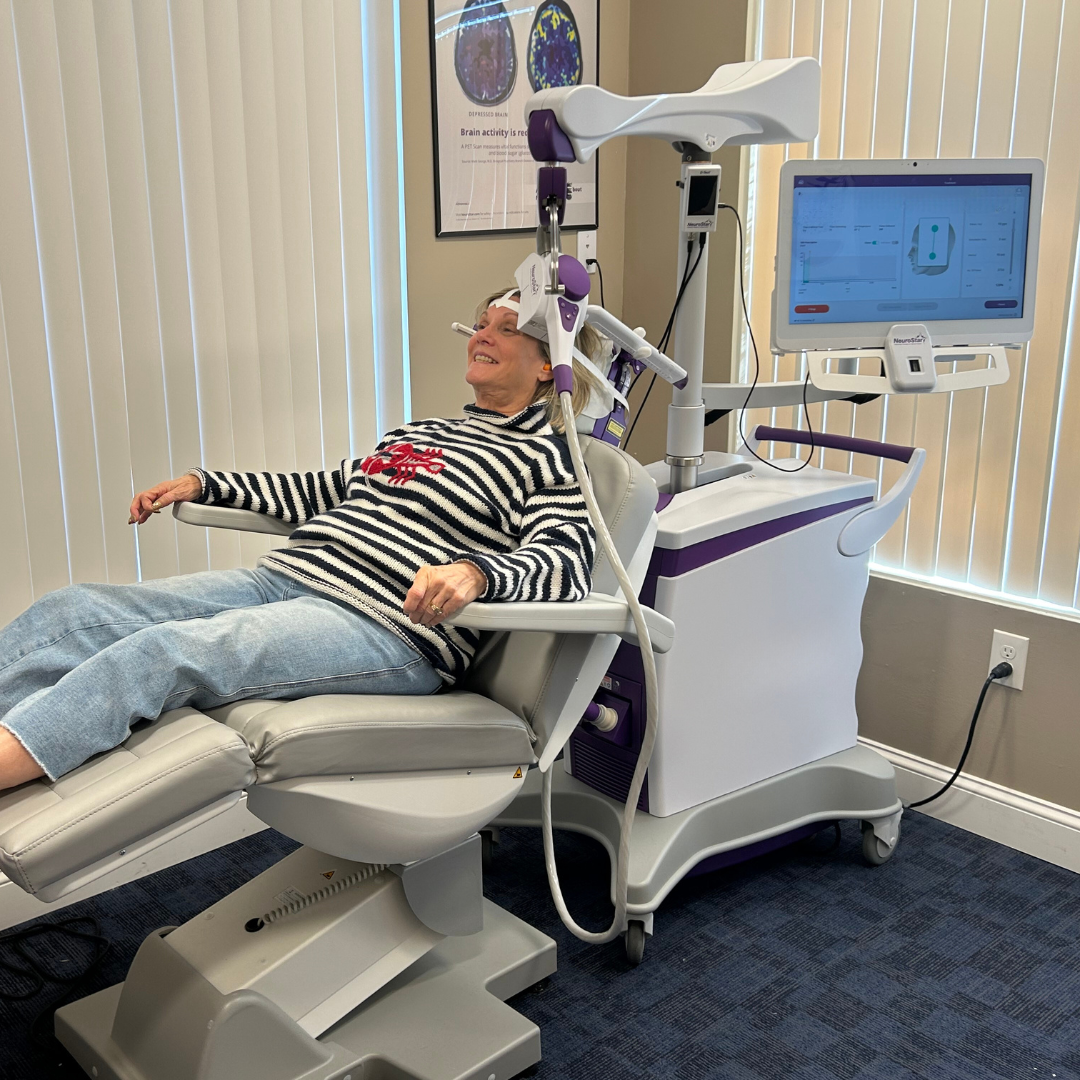
A typical course of TMS therapy involves daily weekday sessions lasting about 20-25 minutes over six-eight weeks. During the procedure, the patient sits in a comfortable chair, and a technician places the TMS coil against the scalp.
The device then emits short magnetic pulses, which might feel like a tapping or “twitching” sensation on the scalp. Patients are awake and alert throughout the procedure, allowing them to immediately return to their daily activities afterward.
Benefits of TMS Therapy
One of the most compelling aspects of TMS therapy is that it is non-invasive, does not require sedation, and patients can resume their normal activities immediately after each session.
Moreover, TMS has a favorable side effect profile, with the most common side effects being scalp discomfort during sessions and mild headaches.
Patient Stories about TMS Therapy
Many patients have shared transformative stories about their experiences with TMS therapy.
Individuals who had struggled with depression for years, finding little to no relief from traditional medications and therapies, have reported significant improvements in their symptoms and quality of life after undergoing TMS.
These personal accounts underscore the potential of TMS to change lives, offering a new lease on life to those who had lost hope in finding effective treatment.
Future Potential for TMS
The future of TMS therapy is bright, with ongoing research aimed at enhancing its effectiveness and expanding its applications.
Advances in imaging technologies, such as functional MRI (fMRI), are helping researchers better understand how TMS affects the brain, paving the way for more targeted and effective treatments.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation therapy is a groundbreaking development in the field of mental health treatment. Its non-invasive nature, combined with a favorable side effect profile, makes it a compelling option for individuals struggling with depression and other mental health conditions.
As research continues to unravel the mechanisms behind TMS and its potential applications broaden, we can anticipate this innovative therapy to play an increasingly vital role in the treatment landscape.
For those seeking alternatives to traditional treatments, TMS represents a beacon of hope, a testament to the relentless pursuit of better, more effective mental health interventions.
